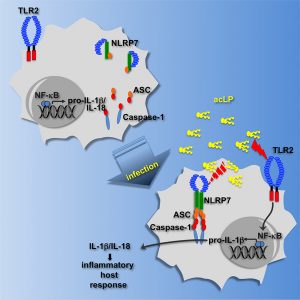
NLRP7 inflammasome
By RNAi screen, we discovered the NLRP7 inflammasome in human macrophages. NLRP7 senses bacterial acylated lipopeptides, which requires its LRRs and is crucial in eliminating infection by Gram positive bacteria, including Staphylococcus aureus and Listeria monocytogenes and Mycoplasma spp. Upon lipopetide sensing, NLRP7 oligomerizes and assembles an ASC and caspase-1-containing inflammasome, resulting in maturation of IL-1b and IL-18.
NLRP7 oligomerization is mediated by its NACHT domain and requires ATP binding and hydrolysis. NLRP7 functions in collaboration with TLR2, where TLR2 is necessary for inflammasome priming and NLRP7 for caspase-1 activation and cytokine release. NLRP7 is one of the NLRs encoded in humans, but not in mice.
Hereditary mutations in NLRP7 are linked to hydatidiform mole (HM), which is a form of trophoblastic neoplasia characterized by cystic degeneration of the chorionic villi and abnormal or lack of embryonic growth and eventually develops into gestational choriocarcinoma, a highly aggressive cancer. We demonstrated that several common HM-linked NLRP7 mutations show hyperactive inflammasome activation, raising the possibility that these mutations represent gain-of-function and that excessive inflammation may contribute to HM. Studies to dissect the mechanism of NLRP7 inflammasome activation, function and signaling during inflammation and microbial infection are ongoing.
References
Khare S, Dorfleutner A, Bryan NB, Yun C, Radian AD, de Almeida L, Rojanasakul Y, Stehlik C. An NLRP7-containing inflammasome mediates recognition of microbial lipopeptides in human macrophages. Immunity 2012, 36, p464-476. PMID:22361007 | pdf
Radian AD, Khare S, Chu LH, Dorfleutner A*, Stehlik C*. ATP binding by NLRP7 is required for inflammasome activation in response to bacterial lipopeptides. Molecular Immunology 2015, 67, p294-302. PMID:26143398 | pdf
Radian AD, de Almeida L, Dorfleutner A*, Stehlik C*. NLRP7 and related inflammasome activating pattern recognition receptors and their function in host defense and disease. Microbes and Infection 2013, 15, p630-639. PMID:23618810 | pdf
Carriere J, Dorfleutner A*, Stehlik C*. NLRP7: From inflammasome regulation to human disease. Immunology 2021, 163, p363-376. PMID:34021586 | pdf
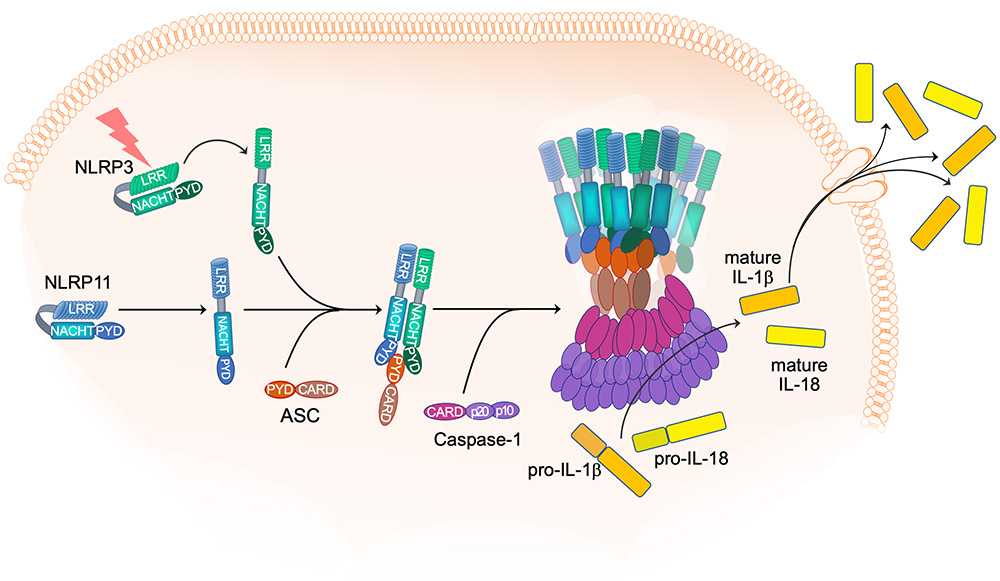
NLRP3 inflammasome
By CRISPR/Cas9, we discovered an essential role of NLRP11 in NLRP3 inflammasome activation in human macrophages. NLRP11 interacts with NLRP3 through NACHT-LRR interactions and with ASC by PYRIN domain (PYD)-PYD interaction, and deletion of NLRP11 specifically prevents NLRP3 inflammasome activation by preventing inflammasome assembly, NLRP3 and ASC polymerization, caspase-1 activation, pyroptosis and cytokine release, but does not affect other inflammasomes. Restored expression of NLRP11, but not NLRP11 lacking either the PYD, the NACHT domain, or the leucine rich repeat (LRR), restores inflammasome activation. NLRP11 is also necessary for inflammasome responses driven by NLRP3 mutations that cause cryopyrin-associated periodic syndrome (CAPS). NLRP11 is not expressed in mice and our discovery therefore emphasizes the specific complexity of inflammasome regulation in humans.
References
Gangopadhyay A, Devi S, Tenguria S, Carriere J, Nguyen H, Jäger E, Khatri H, Chu LH, Ratsimandresy RA, Dorfleutner A*, Stehlik C*. NLRP3 licenses NLRP11 for inflammasome activation in human macrophages. Nature Immunology 2022, 23, 892-903. PMID:35642062 | pdf